V2X is a vehicular technology system that enables vehicles to communicate with the traffic and the environment around them, using short-range wireless signals. Intelligent transportation systems (ITSs) refer to services to improve traffic safety and increase efficiency.
There are two types of V2X communication technology depending on the underlying technology being used:
- WLAN-based
- cellular-based
IEEE first published the specification of WLAN-based V2X (IEEE 802.11p) in 2012. It supports direct communication between vehicles (V2V) and between vehicles and infrastructure (V2I). This technology is referred to as Dedicated Short Range Communication (DSRC). DSRC uses the underlying radio communication provided by 802.11p.
In 2016, 3GPP published V2X specifications based on LTE as the underlying technology. It is generally referred to as “cellular V2X” (C-V2X) to differentiate itself from the 802.11p based V2X technology. In addition to direct communication (V2V, V2I), C-V2X also supports wide-area communication over a cellular network (V2N).
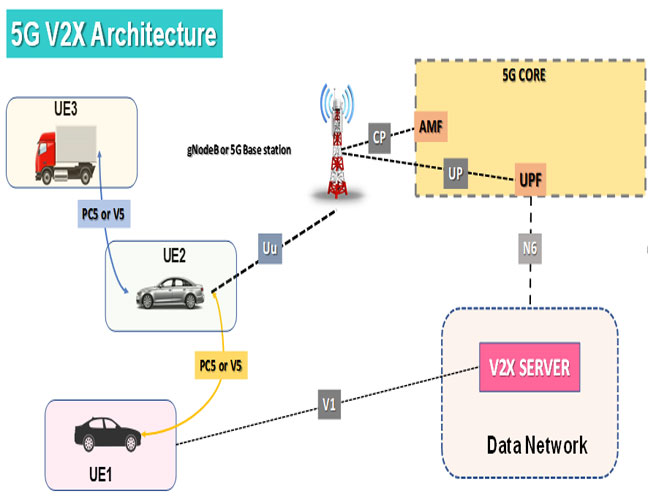
In particular, the third generation partnership project (3GPP) has considered two communication modes:
- Direct vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications
- infrastructure-based V2V communications
The infrastructure-based communication mode is known as Uu-based V2V, and is based on the so-called Uu interface, which is the conventional long-term evolution (LTE) radio interface for uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) communications between UEs and the base stations (BSs) of the radio access network (RAN).
- Using PC5 to directly send and receive V2X messages for UEs who are in close proximity.
- Using unicast for sending messages to the network(application server) using the LTE-Uu interface and then receiving messages using MBMS. this is used when UEs are not in close proximity.
Types of V2X application support in 3GPP
The V2X applications in the present specification, referred to as Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X), contain the following four different types:
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V)
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I)
- Vehicle-to-Network (V2N)
- Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P)








Comments
Comments are closed.