With the rapid development of mobile Internet and Internet of Things(IoT), Telecom services have been increasingly multifarious.
The three main usage scenarios for 5G, namely
1. enhanced Mobile Broadband(eMBB) 2. massive Machine Type of Communication(mMTC) 3. ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication(uRLLC),
However, in terms of performance, the current 4G system cannot meet the requirements of high peak data rate greater than 10 Gbps, 100 Mbps cell-edge data rate and 1 msec end-to-end latency.
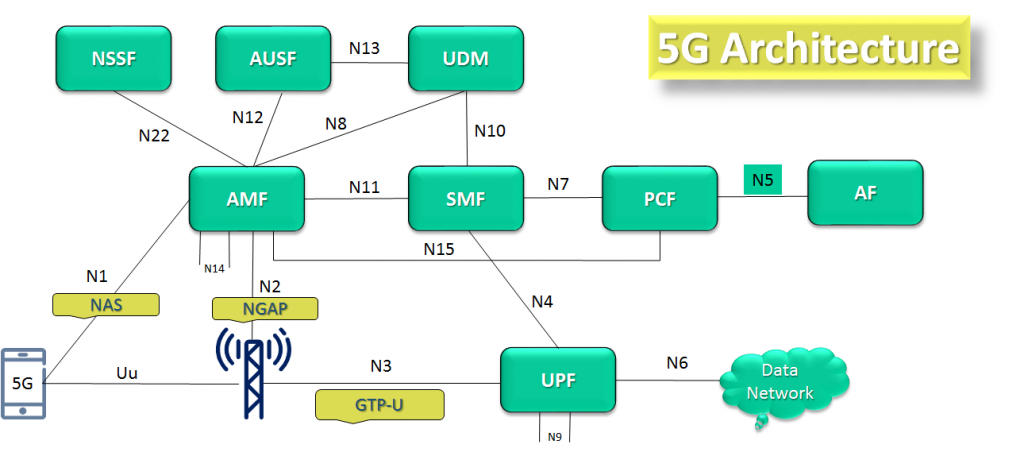
In 5 Each interface has an associated protocol which is used to exchange data between the involved nodes in a way understandable for both sides. 1. NAS Protocol 2. NGAP 3. GTP-U
TheNAS protocol is responsible for exchanging core network messages between the CN and the UE.
The NGAP protocol is responsible for exchanging control messages between RAN and Access Management Function (AMF) via the N2 interface, for example, during the Service Request procedure described later in this section.
While the NGAP is for control plane message exchange, the GTP-U protocol is used for user data delivery betweenRANandUser Plane Function (UPF).
Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) AMF including the termination of RAN CP interface (N2) and of the NAS interface (N1).
| • NAS Signalling Termination |
| •NAS Signalling Security |
| • AS Security Control |
| •Inter CN Node Signalling For Mobility Between 3GPP Access Networks |
| •Idle Mode UE Reachability (Including Control And Execution Of Paging Retransmission) |
| •Registration Area Management |
| •Support Of Intra-system And Inter-system Mobility |
| •Access Authentication |
| •Access Authorization Including Check Of Roaming Rights |
| •Mobility Management Control (Subscription And Policies) |
| •Support Of Network Slicing |
| •SMF Selection |
Session Management Function (SMF) The SMF is connected to the UPF via the N4 interface
| UE IP address allocation and management |
| Selection and control of UP function |
| Configures traffic steering at UPF to route traffic to proper destination |
| Control part of policy enforcement and QoS. |
| Downlink Data Notification |
User Plane Function (UPF), UPF is connected to gNB via N3 interface
| 1.Anchor point for intra‐and inter‐RAT mobility. |
| 2.External PDU session point of interconnection |
| 3.Packet routing and forwarding |
| 4.UP QoS handling |
| 5.Packet inspection and policy rule enforcement |
| 6.Lawful interception |
| 7.Traffic accounting, and reporting. |
| Authentication Server Function (AUSF) (AUSF) supports authentication for 3GPP access and un-trusted non-3GPP access (e.g. toWLAN). |
| Providing authentication |
| Authorization functionalities |
Policy Control Function (PCF)
| Ensures policy and charging control for service data flows |
| Provides authorized Quality of Service [QoS] for a SDF) |
| (PDU) Session related policy control and event reporting. |
Unified Data Management (UDM)
| Supporting The Authentication Credential Repository |
| Processing Function |
| Storing The Long‐term Security Credentials And Subscription Information |
| Access Authorization, Storage, |
| Management Of Privacy-protected Subscription Identifiers |
Application Function (AF),
| Representing any additional CP function which might be required by specific network slices, and which is potentially provided by third parties |
| Application Function (AF) interacts with the 3GPP Core Network in order to provide additional network services |
Radio Access Network
| •Functions for Radio Resource Management: Radio Bearer Control, Radio Admission Control, Connection |
| •Mobility Control, Dynamic allocation of resources to UEs in both uplink and downlink (scheduling) |
| •IP header compression, encryption and integrity protection of data |
| •Selection of an AMF at UE attachment when no routing to an AMF can be determined from the information provided by the UE |
| •Routing of User Plane data towards UPF(s) |
| • Routing of Control Plane information towards AMF |
| •Connection setup and release |
| •Functions for Radio Resource Management: Radio Bearer Control, Radio Admission Control, Connection |
| •Mobility Control, Dynamic allocation of resources to UEs in both uplink and downlink (scheduling) |
| •- IP header compression, encryption and integrity protection of data |
| •- Selection of an AMF at UE attachment when no routing to an AMF can be determined from the information |
| •provided by the UE |
| •Routing of User Plane data towards UPF(s) |
| •Routing of Control Plane information towards AMF |
| Connection setup and release |
Network Slice Selection Function (NSSF) provides slice management functionality
NSSF providing means to collect, store and securely expose the services and capabilities provided by 3GPP NFs, e.g., to third parties or amongst NFs themselves.
Check LTE architecture from https://cafetele.com/lte-architecture/
Check 5G NR network fucntion https://cafetele.com/5g-nr-network-function/
http://www.sharetechnote.com/ Support from sharetecnote,