5G NR Frame Structure
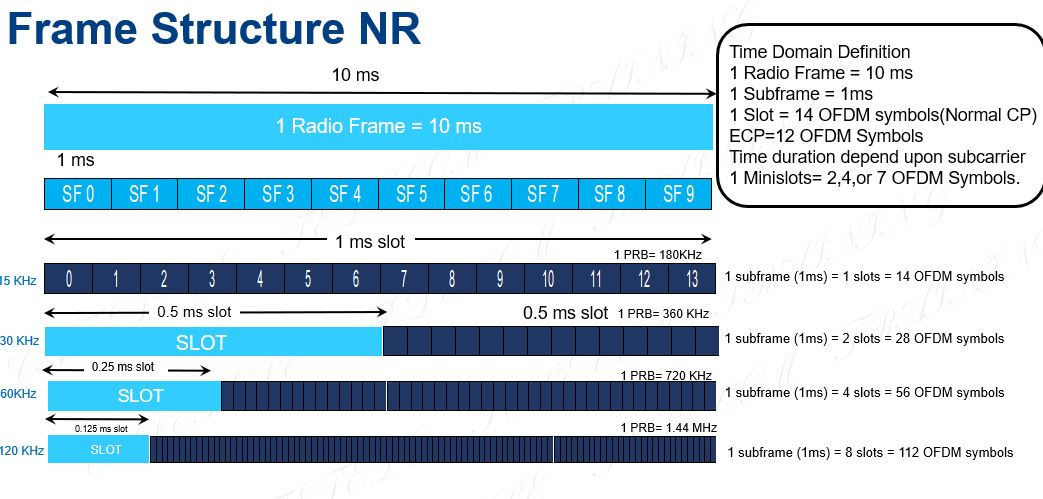
Frame Structure 5G-NR In NR, similar to LTE, a radio frame is fixed to be 10 ms, which consists of 10 subframes each of 1ms. However, different from LTE which has a fixed subcarrier spacing (SCS) for 15 kHz, NR supports scalable numerology for more flexible deployments covering a wide range of services and carrier…